Metopic Suture Synostosis (Trigonocephaly)
What Is Trigonocephaly?
What is trigonocephaly? Trigonocephaly is a rare type of craniosynostosis that occurs when the metopic suture (a seam in the forehead) in a baby’s skull closes prematurely before or shortly after birth. This leads to a triangular-shaped forehead. The head shape often becomes significantly abnormal due to issues with the development of the frontal lobes. When diagnosed early, the treatment process can lead to positive outcomes.Causes of Trigonocephaly
Trigonocephaly may be caused by a specific genetic mutation or environmental factors. Although the exact cause is still unknown, some studies suggest that certain medications taken during pregnancy (particularly epilepsy drugs like sodium valproate) may influence this condition. Additionally, genetic factors are believed to affect brain development.Symptoms of Trigonocephaly
The most distinct feature of trigonocephaly is the triangular shape of the skull. The forehead typically appears pointed, and the distance between the eye sockets is significantly reduced. This can cause the eyes to appear closer together, potentially leading to certain vision problems. The early closure of the metopic suture may increase intracranial pressure, leading to various developmental delays.This skull deformity may sometimes cause headaches or general discomfort. Since the normal development of underlying tissues is also affected, babies born with trigonocephaly must be carefully monitored. If left untreated, this condition can lead to problems in intelligence or overall development later in life.Diagnostic Methods
Trigonocephaly is typically diagnosed through physical examination. Doctors evaluate the typical facial appearance and skull deformity to make a diagnosis. Additionally, imaging tests such as X-ray, CT, or MRI may be required. These imaging methods are helpful in assessing the condition of the bones and identifying potential complications.Trigonocephaly may lead to a range of health issues, especially affecting eye and brain development. Therefore, seeking medical assistance when symptoms are noticed is crucial. Understanding trigonocephaly in detail can help families grasp the condition and explore appropriate treatment options.What Are the Symptoms of Trigonocephaly?
Trigonocephaly is a type of craniosynostosis resulting from the early closure of the metopic suture. This condition affects the structure and appearance of the baby’s skull. Symptoms of trigonocephaly often become apparent from birth and may include the following:- Changes in Skull Shape:
- Closure of the metopic suture in the front of the skull causes the forehead to appear triangular. This characteristic head shape is referred to as “trigonocephaly.”
- The forehead may protrude upward, making the symptoms more noticeable.
- Eye Positioning:
- The distance between the eye sockets is usually narrower than normal, causing the eyes to appear closer together. This can lead to a condition called hypotelorism.
- Facial Asymmetry:
- Facial asymmetry is often observed in individuals with trigonocephaly, especially affecting the symmetry of the cheeks and jaw.
- Developmental Delays:
- Some children may experience overall developmental delays due to trigonocephaly. This may manifest as delayed motor skills, language development, or social interaction.
- Effects on Brain Development:
- The skull deformity can negatively impact brain development. Some children may show signs of slowed cognitive development in early stages. However, this effect may vary from person to person.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Changes in Skull Shape | Triangular shape of the forehead, noticeable protrusions in the front part of the skull. |
| Eye Positioning | Close-set eyes due to reduced distance between the eye sockets; possible hypotelorism. |
| Facial Asymmetry | Lack of symmetry in facial features, particularly in the cheeks and jaw. |
| Developmental Delays | Slower-than-normal development in motor and language skills. |
| Effects on Brain Development | Potential impact on brain growth due to the skull deformity. |
How Is Trigonocephaly Diagnosed?
After answering the question what is trigonocephaly?, the diagnostic process becomes equally important. Trigonocephaly is a cranial deformity caused by the early closure of the metopic suture. The diagnostic process typically includes the following steps:- Physical Examination: The doctor carefully examines the shape of the head to assess whether it deviates from the norm. For early diagnosis, abnormal skull shapes and distinctive features in the baby’s head are closely monitored. A triangular forehead appearance is a key indicator.
- Imaging Tests: To evaluate the internal structure of the skull, doctors often use advanced imaging techniques such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These tests provide detailed information about the condition of the bones and brain development. Asymmetry or other abnormalities of the skull—common trigonocephaly symptoms—can be confirmed through these methods.
- Genetic Evaluation: Since trigonocephaly can sometimes be associated with genetic factors, doctors may recommend genetic testing. However, no specific gene mutation has been identified to definitively confirm the diagnosis. Family history may be assessed to evaluate the likelihood of genetic transmission.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: The diagnostic process is typically carried out by a team of pediatricians, neurologists, and pediatric neurosurgeons. This ensures that both physical and developmental aspects are properly addressed.
Treatment and Management of Trigonocephaly
What is trigonocephaly? It is a condition that occurs when the metopic suture (forehead seam) in a baby’s skull closes prematurely. The primary goal of the treatment process is to ensure proper skull development and support brain growth. Trigonocephaly treatment usually requires surgical intervention. Below are details about treatment methods, applied procedures, and patient follow-up.Surgical Options
There are two main surgical techniques used in the treatment of trigonocephaly: endoscopic surgery and open surgery.| Surgical Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Endoscopic Surgery | A minimally invasive procedure performed to reshape the bones. Small incisions are made in the skull, and helmet therapy is typically combined. This method results in less blood loss and a shorter recovery period. |
| Open Surgery | A traditional method involving opening a large portion of the skull and reshaping it. Typically used in more severe cases, with a longer recovery period. Helmet therapy may also be used post-surgery. |
Treatment Process
- Surgery Timing: These surgeries are typically performed between the ages of 2 months and 1 year. Early intervention is critical for normal brain and skull development. Treatments performed during this period usually yield better results.
- Helmet Therapy: Helmet therapy applied after surgery helps the skull form into the correct shape. The helmet is typically used for 6–9 months, depending on the doctor’s recommendation. It is custom-designed based on precise measurements of the baby’s head.
Long-Term Follow-Up
Short-term observation may not be sufficient for treating trigonocephaly. Long-term follow-up is essential. To monitor post-operative development:- Regular Checkups: Babies should be monitored regularly at every stage of the treatment process. The shape and size of the head should be assessed by the doctor.
- Developmental Assessment: Developmental delays may occur within the first three months. Therefore, it is important to work closely with pediatric specialists to monitor progress.
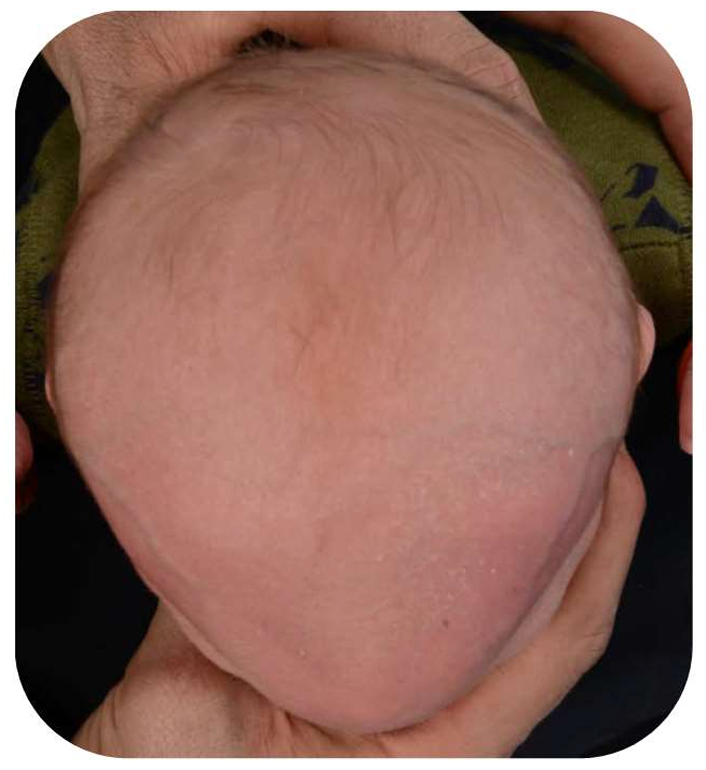
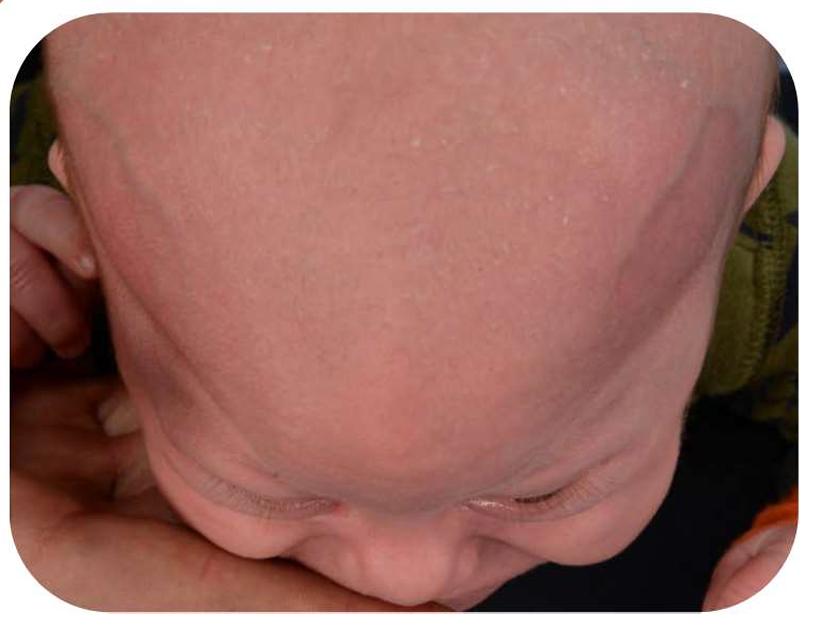
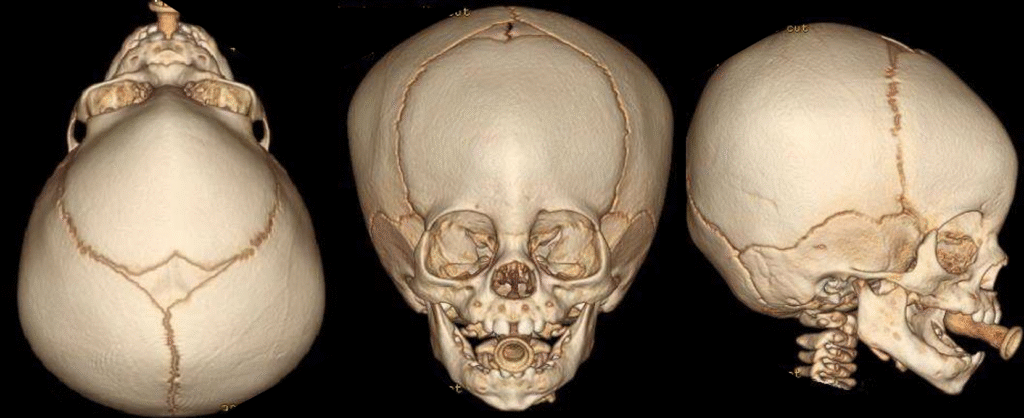
Trigonocephaly is a type of craniosynostosis that occurs as a result of the premature closure of the metopic suture. This condition leads to a congenital head shape deformity and causes the forehead to take on a triangular appearance. The metopic suture is the seam that runs from the top of the forehead down to the bridge of the nose. When this suture closes too early, it causes the skull to develop in an abnormal shape.
The main symptoms of trigonocephaly include a triangular-shaped forehead, eyes positioned closer together than normal, and an abnormally shaped skull. Additionally, some children may experience developmental delays as a result of the condition. Since there can be noticeable differences in the child’s physical appearance, evaluation by a physician is essential.
Trigonocephaly is usually diagnosed through a physical examination. A doctor can make the diagnosis by evaluating the characteristic appearance of the child's skull. In some cases, imaging methods such as X-ray, CT, or MRI may also be used. These tests help determine the structure of the skull and the severity of the deformity.
Do you have any questions?
Didn’t find the answer you were looking for? Get in touch with our expert team—we’d be happy to help!
