Sagittal Suture Synostosis (Scaphocephaly)
What Is Scaphocephaly?
Scaphocephaly is one of the congenital head shape deformities and represents one of the most common types of craniosynostosis. This condition is characterized by abnormal elongation of the skull due to early closure of the sagittal suture. The sagittal suture is the seam located at the top of the skull that joins the two halves of the skull. Symptoms of scaphocephaly include a long and narrow head shape. This change in the baby’s skull can lead over time to noticeable indentations at the back of the head and a forward protrusion in the forehead.Scaphocephaly is more frequently seen in male infants and is usually noticeable at birth. Early diagnosis is crucial for successful treatment. If left untreated, it can negatively impact brain development, causing the normally growing brain to become constricted within a narrow skull, leading to various developmental issues.Treatment for this condition typically involves surgical intervention. The treatment plan varies depending on the severity of the condition and the baby’s age. Since scaphocephaly can lead to long-term neurological problems if not addressed promptly, the skull should be continuously monitored and a specialist consulted when necessary. This ensures both physiological and psychological development.Symptoms of Scaphocephaly
Scaphocephaly refers to a condition in infants characterized by abnormal elongation and narrowing of the skull. This condition is often detected a few months after birth and may present with the following symptoms:- Abnormal Head Shape: The baby’s head may appear longer and narrower than normal, with pronounced front and back areas.
- Asymmetry: Loss of symmetry in the skull, often noticeable as unevenness on one side. Differences in the spacing between the eyes may also be observed.
- Forehead Protrusion: Noticeable protrusions in the forehead are common in babies with scaphocephaly, resulting from the abnormalities affecting the skull.
- Changes in Eye Position: Eyes may appear deeper set or positioned higher than usual due to changes in the skull structure.
- Developmental Delays: This abnormal skull formation can adversely affect brain development, potentially causing delays in physical and cognitive development.
- Pain or Discomfort: In some cases, infants may experience headaches or discomfort related to the condition. While these symptoms are more common in adults, they can also be observed in babies.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Abnormal Head Shape | Long and narrow appearance of the skull |
| Asymmetry | Asymmetrical facial appearance |
| Forehead Protrusion | Protrusions in the forehead |
| Changes in Eye Position | Eyes appearing deeper set or higher than normal |
| Developmental Delays | Delays in physical and cognitive development |
| Pain or Discomfort | Headaches or feelings of discomfort |
Treatment Methods for Scaphocephaly
Scaphocephaly typically arises when the infant’s skull undergoes abnormal shape changes. Treatment methods vary based on the severity of the condition and the baby’s age. Here, we will examine the most common methods used for treatment of scaphocephaly:- Surgical Intervention: If scaphocephaly is advanced, surgery is required. The procedure involves reshaping the skull and is usually recommended for infants aged 3–12 months.
- Helmet Therapy: Specially designed helmets are used to correct the shape of the baby’s skull. This method is suitable for infants aged 3–18 months and works by applying gentle pressure to guide the head into a normal shape. Helmet therapy typically lasts between 3 and 18 months.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing follow-up is essential throughout the treatment process to assess the infant’s condition, monitor treatment effectiveness, and minimize potential side effects.
Causes of Scaphocephaly
What is scaphocephaly? Scaphocephaly is a striking condition that affects brain development and skull shape, arising from various causes during the skull bone development phase in infancy. The main factors contributing to scaphocephaly include:| Causes | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | A family history of scaphocephaly can create a genetic predisposition. |
| Environmental Factors | Maternal smoking, alcohol use, and certain medications during pregnancy may play a role. |
| Premature Birth | Preterm infants are at higher risk due to weaker skull bones. |
| Other Cranial or Neurological Conditions | May occur alongside other head deformities or neurological disorders. |
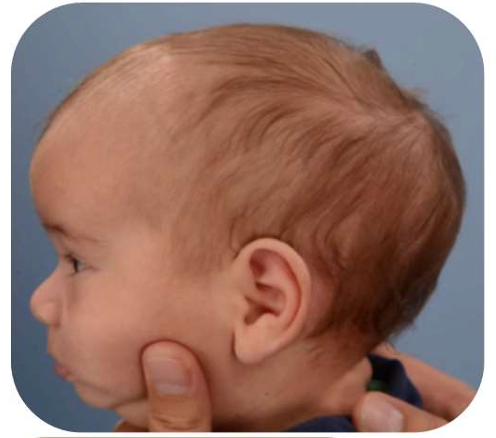
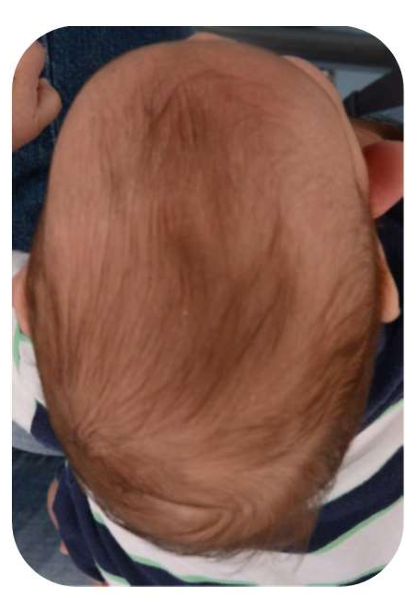
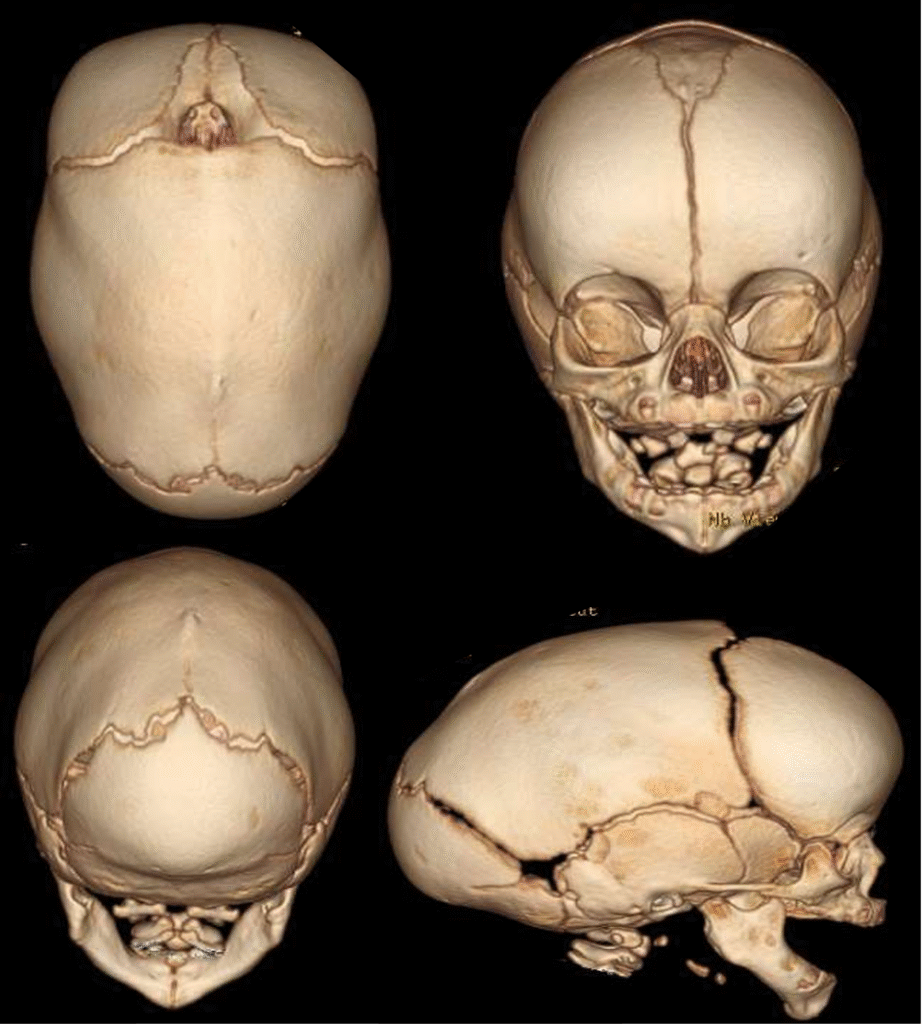
Scaphocephaly is a cranial deformity that occurs as a result of premature closure of the sagittal suture. This condition causes the skull to become long and narrow and is generally more common in male infants. Due to the early closure, brain development may be adversely affected. This abnormality can lead not only to aesthetic concerns but also to increased intracranial pressure and issues related to cognitive development.
Symptoms of scaphocephaly include abnormalities in head shape, disruption of cranial symmetry, and a noticeable protrusion in the forehead. The skull may appear longer and narrower than normal. Additionally, this condition can cause disproportionate eye placement, headaches, and developmental delays. If such symptoms are observed, it is important to consult a healthcare professional without delay.
Scaphocephaly treatment is generally performed through surgical intervention. In early‑diagnosed cases, endoscopic surgery may be applied to open the sagittal suture and restore the normal skull shape. In addition, custom‑designed orthopedic Cranioplus helmets can be used post‑treatment to correct the head shape. The treatment process may vary depending on the child’s health condition.
